Healthy diet and Lifestyle for Diabetic people

Diabetes Mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a metabolic disorder with decreased ability or total inability of the tissues to utilize carbohydrates. The disorder is due to the absence of insulin, its deficiency or ineffectiveness- the hormone is produced by the beta cells in the pancreas. Increasing urbanization, changes in lifestyle, food habits etc have led to the increasing prevalence of diabetes. Around 61.3 million people in India are living with diabetes.
3 main types of DM:
1. Type 1 diabetes -> Unable to produce enough insulin due to loss of beta cells. Mainly found in children and young adults (5-10%).
2. Type 2 diabetes -> begins with insulin resistance (90-95%). Most common form of diabetes.
3. Gestational diabetes- Some pregnant women have higher chances of this diabetes.
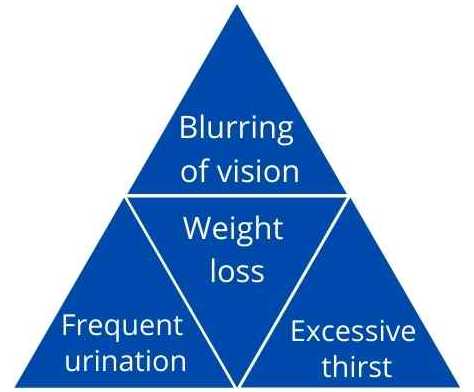
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Tests Diabetic if
Blood sugar levels on Fasting > 120 mg/dl
Blood sugar levels on PP > 180 mg/dl
HbA1C reading >= 6.5
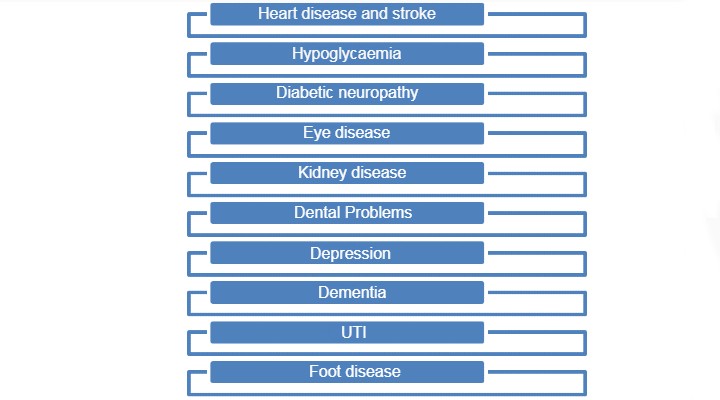
Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes management
Lifestyle management and diet plays a significant role in Diabetes management.
Within 3 months of diagnosis of diabetes or if one is prediabetic then Diabetes can be reversed too under the supervision of a Dietician and an Endocrinologist. Following diabetic diet, increased physical activity, sound sleep and less stress have an overall positive effect.
Diet Management- Diet plays a vital role in management of diabetes as it exerts a direct influence on the blood glucose levels. It should be personalised, based on the nutritional status of the individual.
Food Recommended
1. Diabetics should substitute whole wheat flour with soya flour, whole Bengal flour, barley flour or stalks of green leafy vegetables in the ratio 3:1 is advisable.
2. Whole grams and pulses are preferable to polished ones may be included in at least one meal, can be sprouted or raw form.
3. Salads and boiled vegetables from the group of vegetables allowed i.e. cucumber, radish, tomato, green leafy vegetables, capsicums and gourds.
4. Beverages like rasam, vegetable soup, lime juice, buttermilk etc.
5. Liberal intake of water.
6. Whole wheat bread is preferable to refined flour bread.
7. High fibrous diet is highly recommended.
8. Fenugreek seeds, beans etc have soluble fibres that are found to be more effective in controlling blood sugar levels.
Foods to be taken in limited quantity
1. Cereals like wheat flour, rice and their products like refined flour, bread etc.
2. Variety of refined oils should be taken. Select at least one from each group for your daily cooking purpose. 1:1 per day
a. Group A: sunflower/safflower/corn/soybean
b. Group B: mustard/groundnut/olive
3. Fish/ chicken can be taken in boiled, steamed, grilled or baked form not more than two to three times a month.
4. Egg white can be taken
5. Fruits like orange, sweet lime, apple, papaya, guava, pear may be taken 200-250 grams/day.
6. Skimmed milk may be taken not more than half a litre per day including that needed in curd and other beverages.
7. Beverages like coconut water and tomato juice can be taken in limited amounts.
Food to be avoided
1. Fats like hydrogenated oil, ghee, butter and coconut oil etc.
2. Fried food items i.e. chips, papad, samosa, Puri-paratha etc.
3. Bakery products like cakes, pastries and cream biscuits.
4. Sugar, honey, jam, jaggery, glucose, sweets like laddu, barfi, pudding, desserts, ice creams.
5. Refined starch products like cornflour, commercial jelly products, sabudana, arrowroot powder etc.
6. Vegetables like potato, arbi, tapioca, sweet potato.
7. High calorie fruits like banana, mango, custard apple, Jack fruit, chickoo, leechi, grapes etc.
8. All carbonated drinks, milk shakes, fruit juices etc.
9. Dried fruits and nuts like dates, raisins, groundnuts and coconuts.
10. Malted beverages like boost, bournvita, protinex etc.
11. Fatty meats like ham, bacon, egg yolk, red meat, shrimps, prawns.
12. Canned, tinned, processed and preserved foods to be avoided i.e. sauce, cheese.
13. Pickles made in oil.
General Instructions
• Daily 1 hour brisk walk or exercise.
• Sugar and cholesterol controlled diet plan.
• Avoid injuries specially sensitive areas like skin, feet and hands.
• Get your urine and blood tested regularly.
• Maintain your ideal body weight.
• Reduce your mental tension.
• HDL is very good for heart, whereas LDL and VLDL cholesterol are bad for your heart.
• A high fibre diet is very good for reducing your cholesterol level.